(Last updated on January 15th, 2021)
Visiting some sort of website or another is part of our daily routine. Be it for information purposes, business reasons, online shopping, or the like. Usually, we don’t stop to think whether a site we’re visiting is even safe to browse or not.
Some websites are malicious by design; if we’re not careful, it is easy to fall prey to a phishing or fraudulent site. Even if a website seems to be legit in every respect, remember that about 30,000 websites get hacked every single day.
That means that even if a site was not intentionally infected with malware, hackers could breach the security of a website to use it for their malicious schemes. Even a popular platform like WordPress is one of the most commonly hacked platforms.
Related: 5 Tips to Prevent Malware Infection
Website Hacks
Unsafe websites can open you up to a host of vulnerabilities, including the following cybercrimes:
Phishing Websites
Phishing websites are expertly engineered sites to get visitors to disclose sensitive information like identity or financial details. Phishing is one of the most common cyber-attacks.
These websites can take many forms to appear legitimate in appearance, from an e-commerce website to a replica of another popular site.
Modified Web Content
This is an instance where owing to low security or lack of SSL, third parties get to inject their own content on to websites that do not typically contain that content.
The most common occurrence of this attack is observed over public WiFi hotspots. For instance, in a mall, you might open a regularly visited website, but it will uncharacteristically show a series of pop-up ads.
Pop-ups are invasive enough, but attackers can use this technique to inject malicious content on to a site as well.
Snooping Attacks
This sort of attack is pretty similar to phishing and also most commonly found over public WiFi networks. Also known as sniffing or eavesdropping, this technique is used to steal a user’s private information that is transmitted over a network such as emails, passwords, and even unencrypted messages.
So, in the absence of protection against these attacks, virtually everything you do online is interceptable by an eavesdropper.
Spoofing Attacks
Spoofing websites are designed to impersonate another user or business, tricking the visitors into believing they are interacting with a legit person or company.
Hackers use spoofing attacks to steal sensitive information, gain unauthorized access to systems as well as spread different types of malware.
Fraudulent Websites
These websites are the virtual equivalent of deceitful businesses that used to advertise through brochures or a small newspaper ad.
Usually, the catch is in an extremely low-priced product like a cell phone that you’ve been dreaming of owning but wasn’t able to afford it. If you’re an impulse buyer, your chances of falling victim to such attacks are even higher.
It’s good to remember that these websites are never real and designed to target low-income people.
Malvertising
Malvertising contains malicious ads meant to attract your attention, get you to click on them, and then either be directed to a scam website or download malware.
However, such ads are easy to distinguish as they typically look unprofessional, for the most part. They might even contain spelling or grammar mistakes, unrealistic offers (e.g., an iPhone for $20), celebrity scandals, miracle cures, or product suggestions that don’t fit your browsing history.
Remember that even legitimate ads can be injected with malicious coding, so it’s always best to exercise caution when clicking on a pop-up ad.
So, as we’ve seen, there are countless ways hackers can trick you on unsafe websites. Above, we’ve shared just a few techniques that pan out into hundreds of sub-categories.
That’s why it’s crucial to be wary of a site even if it looks ‘innocent’. Below we share a few tricks and some valuable advice to equip you against such attacks.
Tip # 1: Pay Close Attention to URL Identifier
This is the first part of a URL address called the HyperText Transfer Protocol Source (https). This is an indicator that a website is protected by an SSL certificate that encrypts the sensitive information that a user enters into a banking, shopping, or subscription site, and secures it as it flows from the site to a server.

If a URL starts with ‘http’ instead of https, know that there are dangerous waters ahead. Without SSL, any information that you enter on a site is easily accessible by cybercriminals. Now, https isn’t the fire-sure guarantee against malicious websites, but it’s the first step towards a safe website.
Tip # 2: Scrutinize the URLs
Another quick way of doing your own URL safety check is to hover your cursor over a link given in an email or on a website. The link URL will show in the bottom left-hand corner of your browser if, for instance, you’re using Chrome or Firefox.
Check the URL for misspellings, foreign words, or digits used instead of letters. Hackers know that most people only glance over text while browsing, and they use this tendency to their advantage by developing visuals tricks such as in G00gle instead of Google.

The intention is to get you to leave private or sensitive information on these sites mistaking them for another legit website.
Tip # 3: Presence of Contact Information
Any website that doesn’t have anything to show a physical presence such as a phone number or office address has a by-default element of suspicion.
A safe website is supposed to have all proofs of actual presence like an email address, a phone number, a physical address, social media accounts, and even a return policy (if applicable).
According to a survey report, 54% of respondents wouldn’t trust a website without thorough contact information. And it does make sense too. This information instills a sense of security in the mind of a visitor that they can approach someone if anything goes wrong.
Tip # 4: Look for Privacy Policy
The privacy policy is also a good indicator of a legitimate website, as it shows that the website owner is a law-abiding individual or organization.
The privacy policy shares information about what a website does with user information. Does it keep it strictly confidential or sell it to third parties, etc.? In many countries, it is a legal requirement for websites to publish user privacy terms.
Although privacy policies can be tricky and even genuine, globally popular websites like Facebook can be involved in shady data practices. However, it is still a symbol of legitimacy.
If you find the privacy policy is hard to understand or too lengthy to go over, find relevant information by searching terms like data, retain, rights, store, sell, shared, third parties, etc. This information will inform you about what the website intends to do with your private information.
Tip # 5: Is there a Return Policy?
Just like privacy policy, all eCommerce websites are required to have a return policy or cancellation policy visibly and clearly stated on their site.

This is another trust-building feature and enables the buyers to know the terms and conditions if the need arises for them to return or cancel a product, such as defective merchandise.
You’ll find all reputable eCommerce sites with a return policy as well as a shipping policy. If you don’t see them on a website, it’s best to not shop from them.
Tip # 6: Check the Trust Seals
Trust Seals are the icons termed “Secure” or “Verified”. It indicates that a site works with a security provider to protect the user information as well as its own website from malware infiltration.
These sites usually get regular scans to seek out vulnerabilities and therefore are relatively much safer to interact with than the sites without such assurance.

However, a lot of sites only copy-paste the icons on their web pages to gain the trust of unsuspecting visitors. Therefore, it is advisable to verify the trust seal or badge by clicking on it and seeing where the link takes you.
It should take you to the official website of a security solutions provider with detailed information about the badge and what it entails, clearly mentioned on their page. If it doesn’t, the seal, in all probability, is nothing more than a scam.
Tip # 7: Safe Browsing Tools
All leading web browsers include many security features to ensure that users are safe online while browsing or shopping. There are many extensions available that you can download for added security, as well.
These features help to protect you against a number of vulnerabilities, including pop-up ads, web tracking, harmful downloads, malicious websites, unsafe Flash content, and even control over which sites can access your webcam or microphone.

You can check to see if these features are enabled in your browser’s advanced settings or privacy and security options.
Additionally, you can get advanced browser protection to guard yourself against cyber threats such as targeted advertising, phishing attacks, malware detection as well as identity theft.
Tip # 8: Website Security Check
There are many tools that you can check to see if a website is secure or not if you’re using it for the first time, or you’re unsure about it for any reason. Website safety check tools like Google Safe Browsing or WHOIS offer a quick inspection of sites to inform you about the security status of a website.
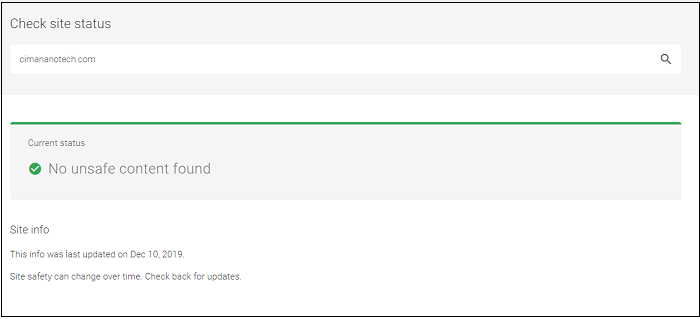
You just have to type in a website’s URL into the search bar of one of these safe browsing sites. The site will test the URL and report you on its credibility within seconds. These are easy to use, quick, and helpful tools. Their effectiveness is especially crucial when you have to enter sensitive information like credit card details on to a site.
Related: Make Your Computer Run Faster! 7 Tips and Tricks
Endnote
In many cases, your search engine like Google will also alert you to unsafe websites with warnings like “This site might be hacked” or “Visiting this site may be harmful to your computer.” In this case, it is best to opt for an alternative site.
But even when they don’t, you now have these simple tricks under your belt to save yourself from harmful websites and potentially dangerous hacking attacks. Just like the real world, caution is a great alley when treading the digital world as well.








